This article describes installing the Elgg social networking engine on Ubuntu Linux with Apache support.
Elgg is an open-source social networking engine framework that makes building and maintaining social networking websites easy.
One may want to install Elgg with Apache on Ubuntu Linux for several reasons.
Firstly, Elgg is an open-source social networking engine that provides a robust framework for building and maintaining social networking websites. It allows for easy collaboration and sharing of ideas among groups such as schools, companies, or communities.
Secondly, Apache is the most popular web server in use, and installing it on Ubuntu Linux allows for hosting multiple websites and applications on a single server.
Lastly, Ubuntu Linux is a highly secure and reliable operating system that provides a stable environment for hosting web applications. By installing Elgg with Apache on Ubuntu Linux, users can take advantage of the security and stability features of both the operating system and the web server, ensuring a safe and smooth experience for social network users.
For more on Elgg’s social platform, please visit its home page
How to install Elgg social networking engine on Ubuntu Linux with Apache support
As described above, Elgg is an open-source social networking engine framework that makes building and maintaining social networking websites for any purpose easy.
Below is how to install it on Ubuntu Linux with Apache.
Install Apache2 HTTP Server on Ubuntu
Apache2 HTTP Server is the most popular web server in use. Install it since Elgg CMS needs it.
To install Apache2 HTTP on the Ubuntu server, run the commands below.
sudo apt update sudo apt install apache2
After installing Apache2, the commands below can stop, start, and enable the Apache2 service to always start up with the server boots.
sudo systemctl stop apache2.service sudo systemctl start apache2.service sudo systemctl enable apache2.service
To test the Apache2 setup, open your browser and browse to the server hostname or IP address. You should see the Apache2 default test page, as shown below. When you see that, then Apache2 is working as expected.
http://localhost

Install MariaDB Database Server
MariaDB database server is a great place to start when looking at open-source database servers for Magento. To install MariaDB, run the commands below.
sudo apt-get install mariadb-server mariadb-client
After installing MariaDB, the commands below can stop, start, and enable the service to start when the server boots.
Run these on Ubuntu 16.04 LTS
sudo systemctl stop mysql.service sudo systemctl start mysql.service sudo systemctl enable mysql.service
Run these on Ubuntu 17.10 and 18.04 LTS
sudo systemctl stop mariadb.service sudo systemctl start mariadb.service sudo systemctl enable mariadb.service
After that, run the commands below to secure the MariaDB server by creating a root password and disallowing remote root access.
sudo mysql_secure_installation
When prompted, answer the questions below by following the guide.
- Enter current password for root (enter for none): Just press the Enter
- Set root password? [Y/n]: Y
- New password: Enter password
- Re-enter new password: Repeat password
- Remove anonymous users? [Y/n]: Y
- Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n]: Y
- Remove the test database and access it. [Y/n]: Y
- Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n]: Y
Restart MariaDB server
Type the commands below to log on to the MariaDB server to test if MariaDB is installed.
sudo mysql -u root -p
Then, type the password you created above to sign on. If successful, you should see a MariaDB welcome message.

Install PHP 7.2 and Related Modules
PHP 7.2 may not be available in Ubuntu default repositories. To install it, you will have to get it from third-party repositories.
Run the commands below to add the below third party repository to upgrade to PHP 7.2
sudo apt-get install software-properties-common sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ondrej/php
Then update and upgrade to PHP 7.2
sudo apt update
Next, run the commands below to install PHP 7.2 and related modules.
sudo apt install php7.2 libapache2-mod-php7.2 php7.2-common php7.2-sqlite3 php7.2-curl php7.2-intl php7.2-mbstring php7.2-xmlrpc php7.2-mysql php7.2-gd php7.2-xml php7.2-cli php7.2-zip
After installing PHP 7.2, run the commands below to open the PHP default config file for Apache2.
sudo nano /etc/php/7.2/apache2/php.ini
Then, save the changes on the following lines below in the file. The value below is an ideal setting to apply in your environment.
file_uploads = On allow_url_fopen = On short_open_tag = On memory_limit = 256M upload_max_filesize = 100M max_execution_time = 360 date.timezone = America/Chicago
After making the change above, please save the file and close it.
After installing PHP and related modules, you must restart Apache2 to reload PHP configurations.
To restart Apache2, run the commands below
sudo systemctl restart apache2.service
To test PHP 7.2 settings with Apache2, create a phpinfo.php file in the Apache2 root directory by running the commands below
sudo nano /var/www/html/phpinfo.php
Then, type the content below and save the file.
<?php phpinfo( ); ?>
Save the file. Then browse to your server hostname followed by /phpinfo.php
http://localhost/phpinfo.php
You should see the PHP default test page.

Create Elgg Database
Once you’ve installed all the packages required for Elgg CMS to function, continue below to start configuring the servers.
First, run the commands below to create a blank Elgg database.
To log on to the MariaDB database server, run the commands below.
sudo mysql -u root -p
Then, create a database called elgg
CREATE DATABASE elgg;
Create a database user called elgguser with a new password
CREATE USER 'elgguser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'new_password_here';
Then, grant the user full access to the database.
GRANT ALL ON elgg.* TO 'elgguser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'user_password_here' WITH GRANT OPTION;
Finally, save your changes and exit.
FLUSH PRIVILEGES; EXIT;
Download and Install Elgg CMS
Run the commands below to download Elgg CMS’s latest content. Then, unzip the download file and move the content to the Apache2 default root directory.
cd /tmp && wget https://elgg.org/download/elgg-2.3.7.zip unzip elgg-2.3.7.zip sudo mv elgg-2.3.7 /var/www/html/elgg
Next, create an Elgg data directory to store data content.
sudo mkdir -p /var/www/html/elgg/data
Next, run the commands below to change the root folder permissions.
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/elgg/ sudo chmod -R 755 /var/www/html/elgg/
Configure Apache2 Elgg CMS Site
Finally, configure the Apache2 configuration file for Elgg CMS. This file will control how users access Elgg CMS content. Run the commands below to create a new configuration file called elgg.conf.
sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/elgg.conf
Then copy and paste the content below into the file and save it. Replace the highlighted line with your domain name and directory root location.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin admin@example.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/elgg
ServerName example.com
<Directory /var/www/html/elgg/>
Options FollowSymlinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
Save the file and exit.
After configuring the VirtualHost above, please enable it by running the commands below.
Enable the Elgg CMS Site
After configuring the VirtualHost above, please enable it by running the commands below, then restart the Apache2 server.
sudo a2ensite elgg.conf sudo a2enmod rewrite sudo systemctl restart apache2.service
Next, open your browser, go to the URL, and continue with the installation.
http://example.com
You should see the Elgg installation wizard page. Click Next to continue.

Validate that PHP requirements are met, enter the database connection info you created above, and continue.

Next, type in the site info, specify the database directory you created above, and continue.
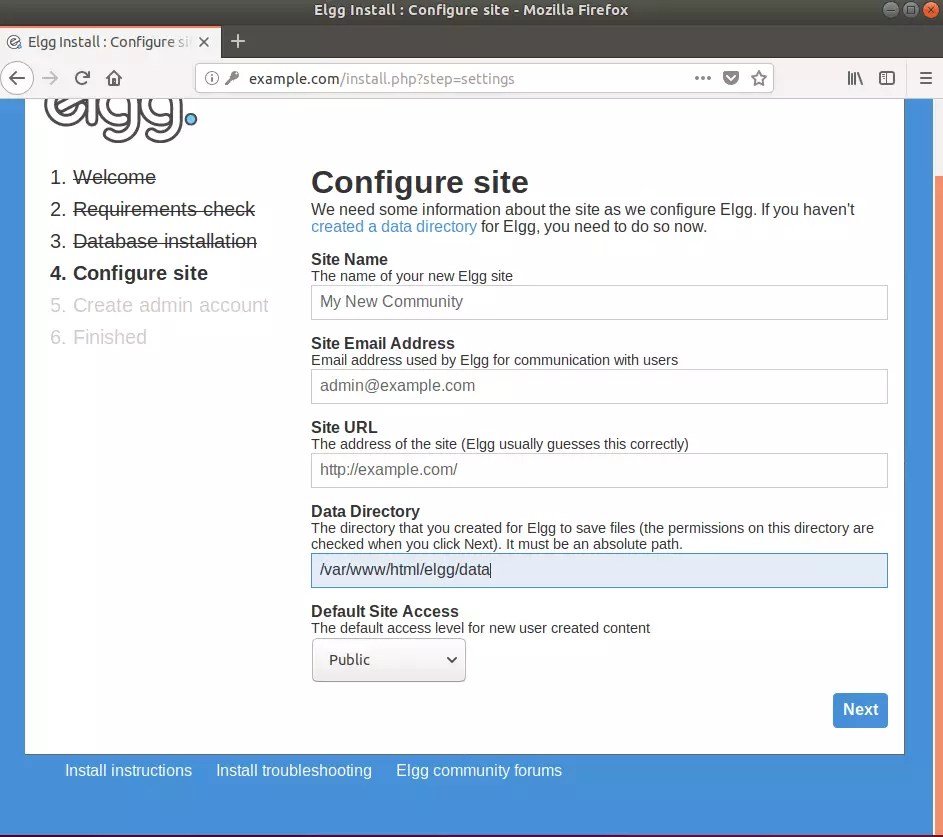
Next, create the admin password and complete the wizard.

After that, Elggshould is installed and ready to use.
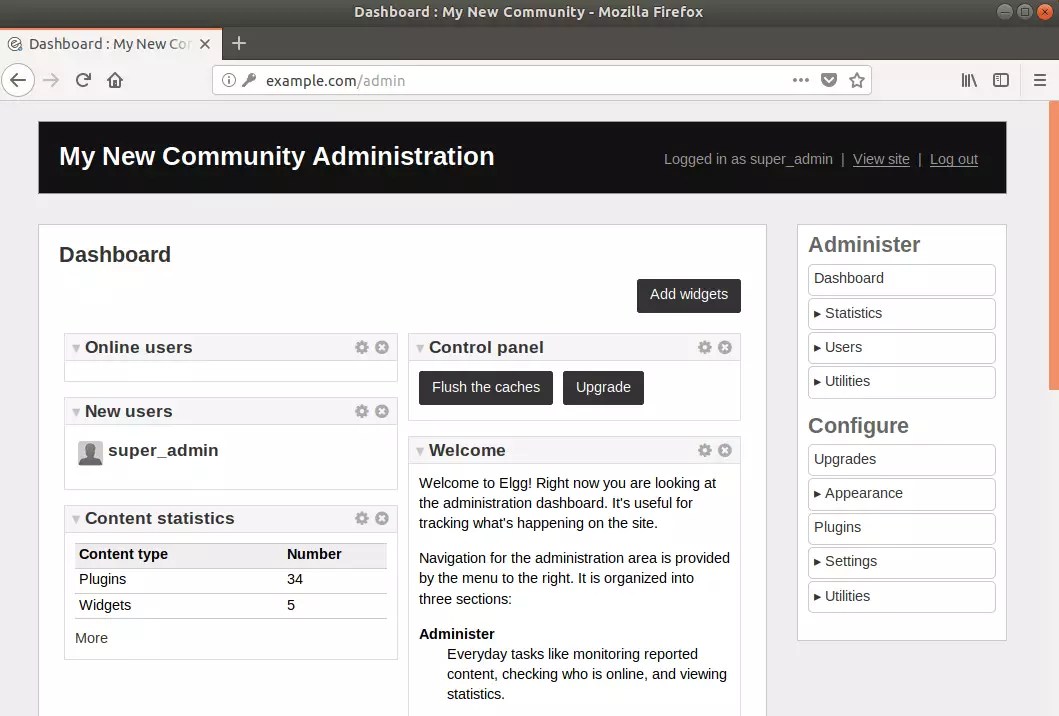
To login to the backend, type the URL below:
http://example.com/admin
Enjoy!
You may also like the post below:
Leave a Reply